
Division of Science and Technology, Taipei Representative Office in Federal Republic of Germany, and Representative Office of MOST (Taiwan), 53175 Bonn, GERMANY
Department of Chemical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, 10607 Taipei, TAIWAN
Toward a universal polymeric material for electrode buffer layers in organic optoelectronics
The first part of the talk will be focused on a novel concept of an electrode buffer layer material, exhibiting either hole transporting or reducing electrode work function (WF) properties, is demonstrated by the example of a polymeric compound PDTON, which can be utilized as a ‘universal’ electrode (either for anode or cathode) buffer layer material. Depending on the composition ratio of acetic acid and ethyl acetate upon dispersing, PDTON forms two kinds of nanospheres, serving as building blocks and defining the morphology and properties of the respective materials, termed as A-PDTON and C-PDTON. These materials are suitable for hole transport (triphenylamine on the surface of A-PDTON nanospheres) and reducing the WF of an electrode due to the formation of a suitable interfacial dipole (C-PDTON), respectively. We demonstrate the versatility and high compatibility of these two types of the same polymer in different devices of organic optoelectronics.
In addition to the scientific presentation, I will give a short introduction about the current collaborations between Taiwan and Germany and the projects which might interest the audiences.
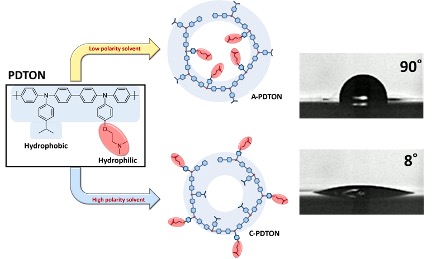
References
- W. T. Wang, J. Sharma, J. W. Chen, C. H. Kao, S. Y. Chen, C. H. Chen, Y. C. Feng, Y. Tai*, Nano Energy, 49, 109-116 (2018)
- Q. Zhang, W. Wang, C. Chi, T. Wächter, J. Chen, C. Tsai, Y. Huang, M. Zharnikov, Y. Tai and D. Liaw*, Energy Environ. Sci., 11, 682-691 (2018)
- W. T. Wang, S. K. Das and Y. Tai*, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 9, 10743-10751 (2017)


























